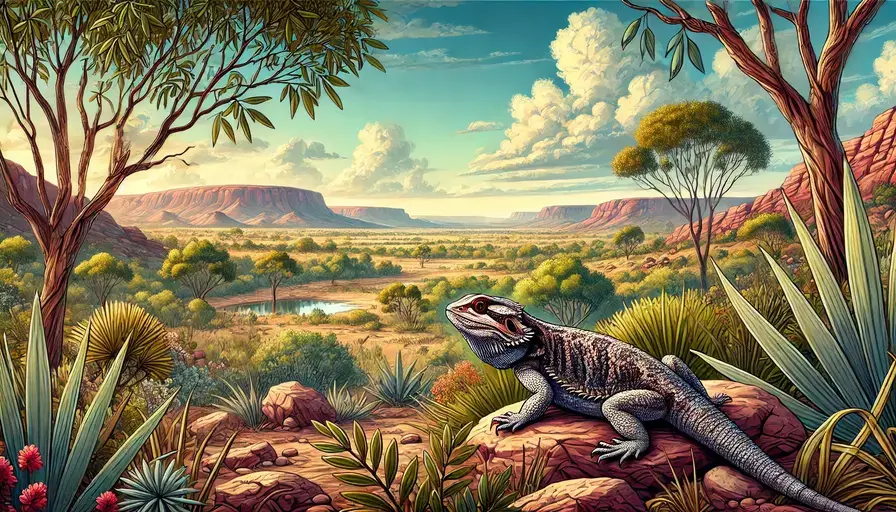
Bearded dragons are among the most popular pet reptiles, but understanding their natural environment can provide valuable insights into their care and behavior.
In this article, we’ll explore the world of the bearded dragon in the wild, including their natural habitat, behavior, and conservation status. Whether you’re a bearded dragon enthusiast or simply curious about these captivating creatures, this guide offers a comprehensive look at their life in the wild.
Where Do Bearded Dragons Live in the Wild?
The bearded dragon in the wild is native to Australia, where they inhabit a variety of environments from arid deserts to semi-arid woodlands. Their natural range includes:
- Central Australia: This region offers a mix of desert and scrubland, ideal for the bearded dragon in the wild to thrive in the harsh, dry conditions.
- Eastern Australia: The open woodlands and rocky outcrops provide suitable habitats for the bearded dragon in the wild.
- Southern Australia: In the southern parts, bearded dragons are found in temperate areas with a combination of grasslands and woodlands.
In these environments, the bearded dragon in the wild is well-adapted to cope with the extremes of Australian weather, including high temperatures and low humidity.

Natural Behavior and Diet
In the wild, the behavior of the bearded dragon is fascinating and diverse:
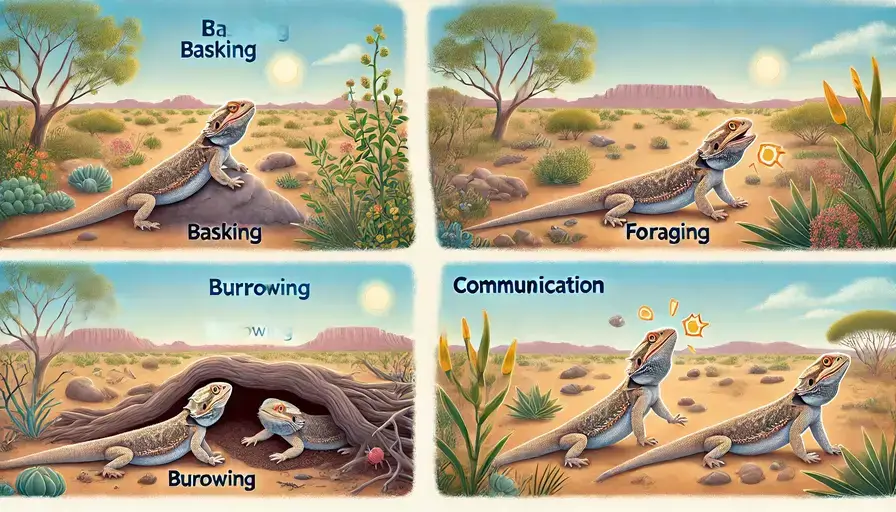
- Basking: The bearded dragon in the wild spends a lot of time basking to regulate its body temperature. They often perch on rocks or branches to absorb the sun’s rays, a behavior that is crucial for their survival.
- Foraging: As omnivores, the diet of the bearded dragon in the wild includes a variety of food sources. They feed on insects, small mammals, and plant material, which includes crickets, beetles, and occasionally small vertebrates, along with leaves, flowers, and fruits.
- Burrowing: To escape the intense heat or evade predators, the bearded dragon in the wild may dig burrows or seek shelter under rocks and logs. This behavior helps them stay cool and protected.
- Communication: Bearded dragons use visual and behavioral signals to communicate. This includes head bobbing, arm waving, and changes in color, which can indicate territoriality, mating readiness, or submission.
Adaptations to the Environment
The bearded dragon in the wild has developed several adaptations to thrive in its environment:
- Coloration: Their coloration helps them blend into their surroundings, providing camouflage against predators. The ability to change color slightly helps regulate their body temperature and signal aggression or readiness to mate.
- Scales: The tough, spiny scales protect them from physical damage and predators, while also helping retain moisture in their arid habitat.
- Metabolism: A slow metabolism allows the bearded dragon in the wild to survive during periods of food scarcity, enabling them to go without food for extended periods if necessary.
Conservation Status
In the wild, bearded dragons are not currently considered endangered. However, their populations are impacted by habitat destruction and climate change. The destruction of their natural habitats due to agricultural expansion, urban development, and other human activities poses a threat to their survival.
How to Care for a Bearded Dragon Pet Inspired by the Wild
Understanding the bearded dragon in the wild can help you provide better care for your pet. Here are some tips inspired by their wild lifestyle:
- Provide a Suitable Habitat: Mimic their natural environment by setting up an appropriate enclosure with basking spots, hiding places, and proper temperature gradients. For more details on setting up a bearded dragon habitat, check out our Bearded Dragon Habitat Guide.
- Mimic Natural Diet: Offer a varied diet that includes live insects and fresh vegetables to replicate their natural foraging behavior and ensure they receive essential nutrients.
- Ensure Proper Lighting: Provide UVB lighting to help your bearded dragon synthesize vitamin D3, which is crucial for calcium absorption, mimicking their exposure to sunlight in the wild.
- Create Enrichment: Include elements in their enclosure that encourage natural behaviors, such as climbing branches and hiding spots.

Internal Links for More Information
For more detailed information on bearded dragons, explore these articles:
- Bearded Dragon for Sale: Learn about the various types and costs of bearded dragons available for purchase.
- Red Bearded Dragon for Sale: Discover the unique characteristics and prices of red bearded dragons.
- Bearded Dragon Habitat Guide: Find comprehensive details on setting up the perfect habitat for your bearded dragon.
- Do Bearded Dragons Bite?: Understand the biting behavior of bearded dragons and how to handle them safely.
Conclusion
Exploring the bearded dragon in the wild provides valuable insights into their natural behaviors and habitat requirements. By understanding their wild environment, you can better care for your pet bearded dragon and create an enriching and suitable home for them.
For more information on bearded dragons, including their care and different types, visit our related articles and guides.

